搜索结果: 1-15 共查到“理学 Global Change”相关记录21条 . 查询时间(0.816 秒)
中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所沈镭、李德龙等在Global Change Biology发表论文揭示植被响应干旱时间尺度的长期变化趋势(图)
沈镭 李德龙 植被响应 干旱时间 尺度 演变 气候
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2024/2/26
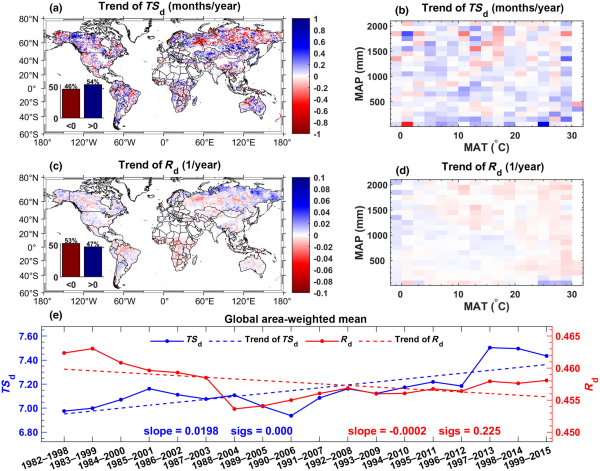
干旱是造成植被死亡的主要驱动因素之一。在未来气候变化下干旱的强度、持续时间和频率会进一步增加,从而导致更高的森林死亡。目前的植被-干旱耦合研究很大程度上被忽视了植被响应干旱的最佳时间尺度(反映植被对干旱敏感性的一个关键指标),要么考虑了干旱时间尺度但忽略了干旱尺度的时间演变趋势,或考虑了植被-干旱敏感性的时间演变趋势而未能考虑干旱时间尺度的影响。在考虑到过去三十年植被对干旱的最佳响应时间后,植被对...

东北地理所在Global Change Biology发文揭示青藏高原沼泽植被秋季物候对气候变化响应机制(图)
青藏高原 气候变化 生态系统
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2024/1/13
植被物候是生态系统响应气候变化的敏感指标。在全球气候变化背景下,植被物候变化会影响生态系统碳循环及水热平衡过程。作为世界上海拔最高的高原,寒冷干旱的青藏高原植被物候是受温度还是水分主导仍然存在争议。青藏高原有大面积的沼泽湿地分布,沼泽相对充裕的水分条件为进一步揭示这一问题提供了理想的条件。明确青藏高原沼泽植被物候时空变化及对气候变化响应机制,能为预测区域碳循环、揭示植被与气候变化关系提供科学依据。...
冉江洪教授课题组在《Global Change Biology》杂志在线发表大熊猫研究成果(图)
冉江洪教授 大熊猫 生命科学学院
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2024/3/5
了解物种的种群趋势和分布范围动态对于全球物种保护至关重要。自人类世以来,随着人类活动强度的持续升级,全球物种遭受了栖息地的急剧丧失和分布范围的缩小。由于大部分原栖息地因人类活动出现各种方式的退化,动物会迁移到新的栖息地以获得更大的生存机会。这种动态的种群分布范围对于物种的生存至关重要,与种群灭绝的概率直接相关。因此,了解种群分布动态变化的机制并识别驱动因素对于预测和指导种群的保护至关重要。

海南大学生态与环境学院胡中民教授在Global Change Biology发表研究论文(图)
海南大学生态与环境学院 胡中民 Global Change Biology 全球气候变化 陆地生态系统
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2022/11/23

浙江大学生命科学学院生态所黄建国教授团队在Global Change Biology上发文阐述温带木本植物的生殖物候策略(图)
黄建国 温带木本植物 生殖物候策略
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2022/10/12
2022年7月28号,浙江大学生命科学学院黄建国教授团队在生态学领域顶级期刊Global Change Biology上发表研究论文“Climate warming leads to advanced fruit development period of temperate woody species but divergent changes in its length”,该研究阐明温带木本植...
兰州大学生命科学学院叶建圣教授在国际著名期刊Global Change Biology发表了两篇生态学研究成果
兰州大学生命科学学院 叶建圣 教授 Global Change Biology 生态学
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2019/8/9
生态学领域国际著名期刊Global Change Biology(IF=8.88)近期接连发表兰州大学与西班牙胡安卡洛斯国王大学、美国耶鲁大学等单位合作的两项生态学原创性研究成果。生命科学学院叶建圣教授为两篇研究论文的第一及通讯作者,兰州大学生命科学学院、草地农业生态系统国家重点实验室为论文第一完成单位。在题为“Multifunctionality debt in global drylands ...
Commission on Tourism, Leisure and Global Change of the International Geographical Union
Big data geographical analytics tourism geography
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2016/7/27
The Objectives of this conference are to provide a platform for tourism students and educators, government agency employees, hospitality and tourism industry practitioners, public and private land man...
West Coast study emphasizes challenges faced by marine organisms exposed to global change
West Coast study marine organisms global change
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2016/1/17
The Pacific Ocean along the West Coast serves as a model for how other areas of the ocean could respond in coming decades as the climate warms and emission of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide incr...
Spread of endemic disease and global change in an educational project: proposition of relationships developed in a twin partnership
win partnership Dengue fever Education to sustainability Global changes Cape Verde
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2015/8/26
The sudden event of the spread of dengue fever (or break-bone fever) that appeared for the first time in Cape Verde in 2009 revealed that inappropriate management of waste can be considered a major ca...
Biotic Response to Global Change: The Last 145 Million Years
145 Million Years Global Change
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2015/7/31
This volume has its origins in a joint research program between the Natural History Museum, London and University College, London on Global Change and the Biosphere. The authors are mainly paleontolog...
Taking the Pulse of Marine Ecosystems: The Importance of Coupling Long-Term Physical and Biological Observations in the Context of Global Change Biology
Coupling Long-Term Physical Biological Observations
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2015/7/16
Research programs that co-locate environmental sensors with "biology" can enable the linking of environmental data with changes in biological or ecological processes. The coastal and marine Long Term ...

戈峰研究组有关二氧化碳浓度升高环境下植物气孔的闭合有助于提高蚜虫取食效率的研究成果在Global Change Biology发表(图)
植物气孔 蚜虫
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2015/6/25
大气CO2浓度升高不仅加剧了全球气候变化,还改变了动植物的生长发育过程。其中,对C3植物最重要的影响是增加了光合作用,并降低气孔导度。而植物气孔导度的降低导致植物蒸腾作用降低,水分利用率增加,对蚜虫这类取食植物韧皮部汁液的刺吸式口器昆虫来说,寄主植物保持相对高的水势和膨压对蚜虫被动取食、获取植物汁液非常重要。在调节水分利用效率和叶片气孔的张开程度过程中,植物脱落酸(ABA)信号途径发挥至关重要的作...
Grassland production under global change scenarios for New Zealand pastoral agriculture
Grassland production global change scenarios
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2014/12/19
We adapt and integrate the Biome-BGC and Land
Use in Rural New Zealand models to simulate pastoral agriculture and to make land-use change, intensification of agricultural activity and climate ...
Alpine lake optical properties as sentinels of dust deposition and global change
Alpine lake optical properties sentinels of dust deposition global change
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2014/4/17
We characterized dissolved organic matter in La Caldera, an alpine lake in Sierra Nevada (Spain), and watersoluble organic compounds (WSOC) in dry and wet deposition originating from Saharan and marin...
Future directions for hydropedology: quantifying impacts of global change on land use
Future directions hydropedology quantifying impacts global change on land use
font style='font-size:12px;'>
2009/9/11
Hydropedology is well positioned to address contemporary issues resulting from climate change. We propose a six-step process by which digital, field-scale maps will be produced to show where climate c...


